In semiconductor manufacturing wet chemical etching – In semiconductor manufacturing, wet chemical etching plays a pivotal role in shaping and defining the intricate patterns that form the foundation of modern electronics. This process involves the controlled removal of material from a semiconductor wafer using a chemical solution, offering unique advantages and challenges compared to other etching techniques.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of wet chemical etching, exploring its types, process parameters, equipment, and applications. We will also examine the environmental and safety considerations associated with this process, ensuring a holistic understanding of its impact on the semiconductor industry.
1. Overview of Wet Chemical Etching in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Wet chemical etching is a process that uses liquid chemicals to remove material from a semiconductor wafer. It is a critical step in semiconductor manufacturing, as it is used to create the patterns and structures that are necessary for device operation.
Wet chemical etching has several advantages over other etching methods, including its ability to achieve high selectivity and control over the etch profile.
However, wet chemical etching also has some disadvantages, such as the potential for contamination and the generation of hazardous waste. Despite these disadvantages, wet chemical etching remains an essential process in semiconductor manufacturing.
2. Types of Wet Chemical Etchants
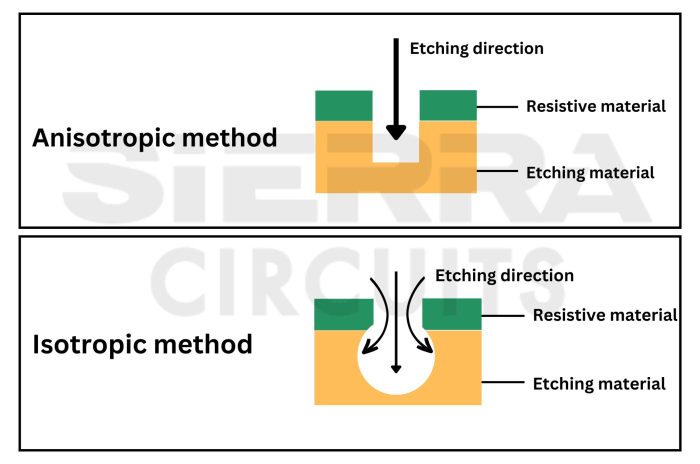
There are two main types of wet chemical etchants: isotropic and anisotropic. Isotropic etchants etch in all directions, while anisotropic etchants etch in a preferred direction. The type of etchant used depends on the desired etch profile.
Some common isotropic etchants include:
- Hydrofluoric acid (HF)
- Nitric acid (HNO 3)
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Some common anisotropic etchants include:
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
- Tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH)
- Ethylenediamine pyrocatechol (EDP)
3. Etching Process Parameters
The wet chemical etching process is influenced by several parameters, including:
- Etchant concentration
- Temperature
- Agitation
The etchant concentration affects the etch rate. A higher concentration of etchant will result in a faster etch rate. The temperature also affects the etch rate, with higher temperatures resulting in faster etch rates. Agitation helps to remove reaction products from the surface of the wafer, which can also increase the etch rate.
4. Etching Equipment and Techniques

There are two main types of etching equipment used in semiconductor manufacturing: batch etchers and single-wafer etchers. Batch etchers process multiple wafers at the same time, while single-wafer etchers process one wafer at a time. Single-wafer etchers are more expensive than batch etchers, but they offer better control over the etch process.
There are several techniques that can be used to improve etch uniformity and control, including:
- Spray etching
- Pulsed etching
Spray etching involves spraying the etchant onto the wafer, which can help to improve etch uniformity. Pulsed etching involves alternating between etching and rinsing steps, which can help to control the etch profile.
5. Applications of Wet Chemical Etching in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Wet chemical etching is used in various stages of semiconductor manufacturing, including:
- Wafer cleaning
- Pattern transfer
- Device fabrication
Wet chemical etching is particularly well-suited for wafer cleaning, as it can remove a wide variety of contaminants. Wet chemical etching is also used to transfer patterns from a mask to a wafer. This process is known as photolithography. Finally, wet chemical etching is used to fabricate devices by etching away unwanted material.
6. Environmental and Safety Considerations
![]()
Wet chemical etching can generate hazardous waste, including acids, bases, and solvents. It is important to properly dispose of this waste to protect the environment. Wet chemical etching can also pose a safety hazard to workers, as the chemicals used can be corrosive and toxic.
It is important to wear proper protective gear and to follow all safety procedures when working with wet chemical etchants.
Question & Answer Hub: In Semiconductor Manufacturing Wet Chemical Etching
What is the primary advantage of wet chemical etching over other etching methods?
Wet chemical etching offers superior selectivity, allowing for precise removal of specific materials while leaving others unaffected.
How does the etchant concentration influence the etching process?
Higher etchant concentrations generally result in faster etch rates, but can also lead to increased underetching and isotropic etching.
What safety measures are necessary when working with wet chemical etchants?
Proper ventilation, protective clothing, and appropriate waste disposal procedures are essential to minimize exposure to hazardous chemicals.