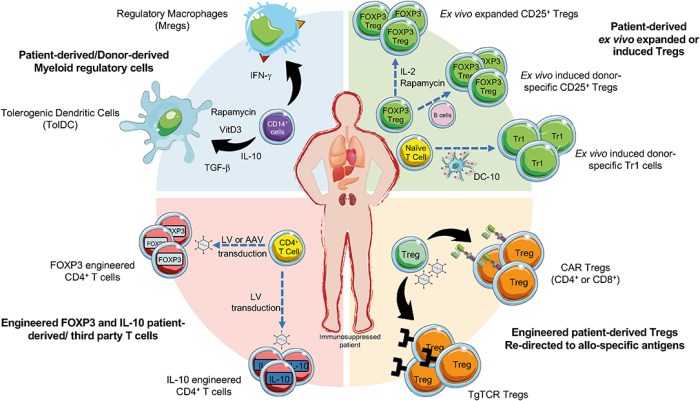
Which best describes the role of immunosuppressants in transplant surgeries – Immunosuppressants play a pivotal role in transplant surgeries, as they effectively suppress the immune system’s response to prevent rejection of the transplanted organ or tissue. This article delves into the mechanisms of action, types, administration, monitoring, and long-term outcomes of immunosuppressant therapy in transplant surgeries.
Understanding the complexities of immunosuppressant therapy is crucial for optimizing transplant outcomes and improving patient survival rates. By delving into the latest advancements in immunosuppressant research and exploring the potential of personalized medicine, we can further enhance the effectiveness of these therapies and improve the quality of life for transplant recipients.
Overview of Immunosuppressants in Transplant Surgeries: Which Best Describes The Role Of Immunosuppressants In Transplant Surgeries
Immunosuppressants are medications used in transplant surgeries to suppress the recipient’s immune system and prevent rejection of the transplanted organ or tissue. The immune system recognizes the transplanted organ as foreign and attacks it, leading to rejection. Immunosuppressants work by inhibiting various immune cells and pathways to prevent this attack.
Immunosuppressants have different mechanisms of action. Some target T cells, which are responsible for recognizing and attacking foreign cells. Others target B cells, which produce antibodies against foreign antigens. Immunosuppressants can also inhibit the production of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that regulate immune responses.
There are several types of immunosuppressants used in transplant surgeries. Calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and cyclosporine, are commonly used to prevent rejection. These drugs inhibit the activation of T cells by blocking the action of calcineurin, a protein involved in T cell signaling.
Role of Immunosuppressants in Preventing Rejection, Which best describes the role of immunosuppressants in transplant surgeries
The immune system plays a crucial role in protecting the body from infections and diseases. However, in the context of organ transplantation, the immune system can recognize the transplanted organ as foreign and launch an attack against it, leading to rejection.
Immunosuppressants are used to suppress the immune response and prevent rejection.
Immunosuppressants work by inhibiting various immune cells and pathways involved in rejection. They can suppress the activation and proliferation of T cells and B cells, which are responsible for recognizing and attacking foreign antigens. Immunosuppressants can also inhibit the production of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that regulate immune responses.
Immunosuppressants are typically administered orally or intravenously. The dosage and duration of treatment vary depending on the type of transplant, the patient’s immune status, and the specific immunosuppressant being used. Regular monitoring of the patient’s immune function and blood levels of the immunosuppressant is essential to ensure adequate suppression of the immune response and prevent rejection.
Management of Immunosuppressant Therapy
Immunosuppressant therapy is a complex and challenging aspect of transplant surgeries. The primary challenge lies in finding the optimal balance between suppressing the immune response to prevent rejection and avoiding excessive immunosuppression, which can increase the risk of infections and other complications.
Patient education and adherence to medication regimens are crucial for the success of immunosuppressant therapy. Patients need to understand the importance of taking their medications as prescribed, even when they feel well. Skipping doses or altering the dosage can compromise the effectiveness of the immunosuppressants and increase the risk of rejection.
Immunosuppressant therapy can have various side effects and complications. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, and increased susceptibility to infections. More severe complications can include kidney damage, liver damage, and an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Long-Term Outcomes of Immunosuppressant Therapy
Immunosuppressant therapy plays a significant role in improving the long-term outcomes of transplant surgeries. By preventing rejection, immunosuppressants help prolong the survival and function of the transplanted organ or tissue. This can lead to improved quality of life and increased life expectancy for transplant recipients.
Immunosuppressants have been shown to reduce the risk of graft failure, which is the failure of the transplanted organ or tissue to function properly. Graft failure can occur due to rejection, infection, or other complications. Immunosuppressants help to prevent rejection and protect the graft from damage, thereby reducing the risk of graft failure.
Studies have shown that immunosuppressant therapy has significantly improved the survival rates of transplant recipients. For example, in kidney transplantation, the 5-year survival rate for patients receiving immunosuppressants has increased from less than 50% in the 1970s to over 90% today.
Advancements in Immunosuppressant Therapy
Research in immunosuppressant therapy is ongoing, with the aim of developing new drugs that are more effective, have fewer side effects, and can be tailored to individual patients. One promising area of research is the development of targeted immunosuppressants that specifically inhibit certain immune cells or pathways involved in rejection.
Another area of research is the use of personalized medicine to optimize immunosuppressant therapy. By analyzing a patient’s genetic profile and immune response, doctors can tailor the type and dosage of immunosuppressants to the individual patient’s needs. This approach can help to minimize side effects and improve the long-term outcomes of transplant surgeries.
FAQ Explained
What are immunosuppressants?
Immunosuppressants are medications that suppress the immune system to prevent rejection of transplanted organs or tissues.
How do immunosuppressants work?
Immunosuppressants work by interfering with the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack the transplanted organ or tissue as foreign.
What are the different types of immunosuppressants?
There are several types of immunosuppressants, including calcineurin inhibitors, mTOR inhibitors, and anti-proliferative agents.
What are the side effects of immunosuppressants?
Immunosuppressants can have side effects such as increased risk of infection, kidney damage, and high blood pressure.
How are immunosuppressants monitored?
Immunosuppressant levels are typically monitored through blood tests to ensure they are within the desired therapeutic range.