Navigating the landscape of retirement accounts can be daunting, but understanding the different options available is crucial for securing your financial future. This guide will delve into the intricacies of compare types of retirement accounts ngpf answers, empowering you to make informed decisions about your retirement savings.
Retirement accounts offer tax benefits and investment opportunities to help you accumulate wealth for your golden years. From traditional IRAs to 401(k) plans and annuities, each type of account has its own unique features and considerations. This guide will explore the key differences between these accounts, providing you with the knowledge to choose the best option for your individual needs.
Overview of Retirement Accounts
Retirement accounts are investment vehicles designed to help individuals save for their future retirement. They offer tax benefits and investment options that can help grow savings over time. There are different types of retirement accounts available, each with its own rules and benefits.
The primary purpose of a retirement account is to provide individuals with a source of income during their retirement years, when they may no longer be able to work. By investing in a retirement account, individuals can take advantage of tax-advantaged savings and investment growth to accumulate funds for their future.
Some of the benefits of retirement accounts include:
- Tax-advantaged savings: Contributions to certain retirement accounts, such as traditional IRAs and 401(k) plans, may be tax-deductible, reducing the amount of taxable income.
- Investment growth: Retirement accounts typically offer a variety of investment options, allowing individuals to choose investments that align with their risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Compound interest: Earnings on investments within retirement accounts are typically reinvested, leading to the potential for exponential growth over time.
- Retirement income: Withdrawals from retirement accounts can provide individuals with a steady source of income during retirement.
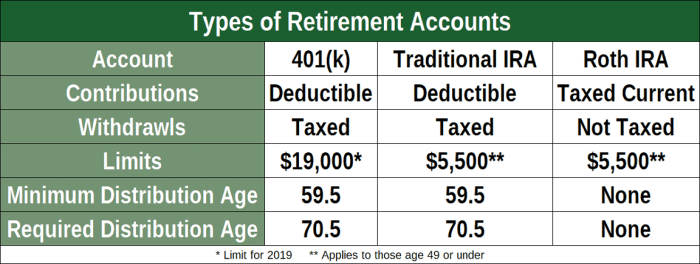
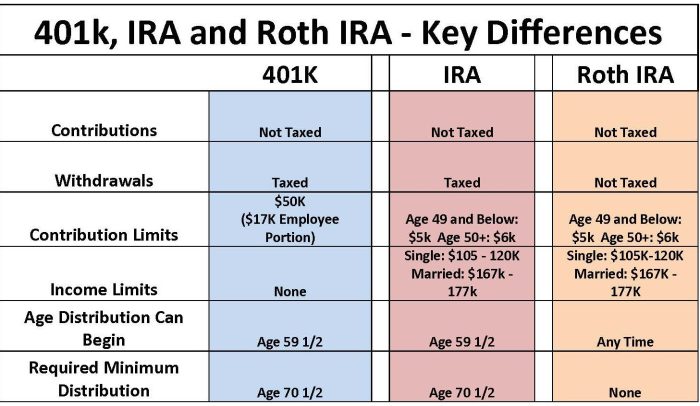
Traditional IRAs vs. Roth IRAs
Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs are two common types of individual retirement accounts. They differ in terms of contribution limits, tax treatment, and income limits.
Contribution Limits
- Traditional IRAs: For 2023, the annual contribution limit is $6,500 ($7,500 for individuals age 50 or older).
- Roth IRAs: For 2023, the annual contribution limit is $6,500 ($7,500 for individuals age 50 or older).
Tax Treatment
- Traditional IRAs: Contributions are tax-deductible, reducing the amount of taxable income in the year of the contribution. Withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
- Roth IRAs: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, meaning they do not reduce taxable income. However, qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
Income Limits
- Traditional IRAs: There are no income limits for making contributions to a traditional IRA. However, there are income limits for deducting contributions on your tax return.
- Roth IRAs: There are income limits for making contributions to a Roth IRA. For 2023, the phase-out range for Roth IRA contributions is $138,000 to $153,000 for single filers and $218,000 to $228,000 for married couples filing jointly.
401(k) Plans vs. 403(b) Plans
401(k) plans and 403(b) plans are employer-sponsored retirement plans that offer tax-advantaged savings. They are similar in many ways, but there are some key differences.
Contribution Limits
- 401(k) plans: For 2023, the annual contribution limit is $22,500 ($30,000 for individuals age 50 or older).
- 403(b) plans: For 2023, the annual contribution limit is $22,500 ($30,000 for individuals age 50 or older).
Employer Matching
- 401(k) plans: Many employers offer matching contributions to their employees’ 401(k) plans. This means that the employer will contribute a certain amount of money to the employee’s 401(k) account for every dollar the employee contributes, up to a certain limit.
- 403(b) plans: Employers are not required to offer matching contributions to their employees’ 403(b) plans. However, some employers may choose to do so.
Vesting Schedules
- 401(k) plans: Employer matching contributions are typically subject to a vesting schedule. This means that the employee must work for the employer for a certain number of years before they are fully vested in the matching contributions. If the employee leaves the employer before they are fully vested, they may forfeit some or all of the matching contributions.
- 403(b) plans: Employer matching contributions to 403(b) plans are typically immediately vested.
Annuities vs. Mutual Funds, Compare types of retirement accounts ngpf answers
Annuities and mutual funds are two different types of investment vehicles that can be used for retirement savings. They have different features, benefits, and risks.
Types of Annuities
- Fixed annuities: Fixed annuities provide a guaranteed rate of return for a specified period of time.
- Variable annuities: Variable annuities offer the potential for higher returns than fixed annuities, but they also carry more risk.
- Indexed annuities: Indexed annuities offer a combination of features from fixed and variable annuities.
Investment Options and Fees
- Annuities: Annuities typically offer a limited range of investment options, such as fixed income investments and money market accounts. Annuities may also have high fees, which can reduce the potential return on investment.
- Mutual funds: Mutual funds offer a wide range of investment options, including stocks, bonds, and real estate. Mutual funds typically have lower fees than annuities.
Potential Returns and Risks
- Annuities: Fixed annuities offer a guaranteed return, but the potential for growth is limited. Variable annuities offer the potential for higher returns, but they also carry more risk. Indexed annuities offer a balance between fixed and variable annuities, with a guaranteed minimum return and the potential for additional growth.
- Mutual funds: The potential return on a mutual fund depends on the performance of the underlying investments. Mutual funds can be more volatile than annuities, but they also have the potential for higher returns.
Choosing the Right Retirement Account
Choosing the right retirement account depends on a number of factors, including:
- Income
- Age
- Risk tolerance
- Investment goals
- Tax situation
It is important to consider all of these factors when choosing a retirement account. A financial advisor can help you assess your individual needs and choose the right account for you.
Diversifying Retirement Savings
It is important to diversify your retirement savings by investing in a variety of asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. This will help to reduce the risk of your portfolio and improve your chances of achieving your retirement goals.
FAQ Compilation: Compare Types Of Retirement Accounts Ngpf Answers
What are the main types of retirement accounts?
The main types of retirement accounts include traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs, 401(k) plans, 403(b) plans, and annuities.
What are the key differences between traditional and Roth IRAs?
Traditional IRAs offer tax-deductible contributions but withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income. Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals but contributions are made with after-tax dollars.
What is the maximum contribution limit for a 401(k) plan?
The maximum contribution limit for a 401(k) plan is $22,500 in 2023, with an additional catch-up contribution limit of $7,500 for individuals age 50 and older.
What is an annuity?
An annuity is a contract with an insurance company that provides a stream of income for a specified period or for the rest of your life.
How do I choose the right retirement account for me?
Choosing the right retirement account depends on your age, income, risk tolerance, and retirement goals. It is recommended to consult with a financial advisor to determine the best option for your individual circumstances.